Understanding the common nail: A Foundation in Construction and Manufacturing
The **common nail** stands as a foundational fastener in construction and manufacturing, essential for securing materials across a vast array of applications. Its robust design and simple yet effective functionality make it indispensable for tasks ranging from structural framing to general carpentry. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate details of **common nail** manufacturing, technical specifications, diverse applications, and the strategic considerations for B2B procurement. We aim to provide an authoritative resource for engineers, project managers, and procurement specialists seeking to optimize their fastening solutions.
From the ubiquitous 6d common nail used in light framing to the heavy-duty 60d nails for structural applications, understanding the nuances of these fasteners is paramount. The evolution of **wire nail manufacturers** has led to advancements in material science and production techniques, ensuring enhanced performance and longevity. This article will also explore the distinction between **wire nails vs common nails**, highlighting the specific advantages and use cases for each type.
Manufacturing Process of **Common Nail**
The production of a **common nail** is a highly automated and precise process, ensuring consistency in quality and performance. The primary material typically used is high-grade carbon steel wire, specifically mild steel wire nail, which offers an optimal balance of strength and ductility. For enhanced corrosion resistance, materials like stainless steel or surface treatments such as galvanization are employed, leading to products like **galvanized round wire nails** or **galvanised nails 75mm**.
Process Flow:
- Wire Drawing: High-carbon steel wire rods are drawn through a series of dies to achieve the desired diameter. This process, often referred to as cold drawing, enhances the tensile strength of the wire.
- Heading: The drawn wire is fed into a nail-making machine. One end of the wire is then mechanically pressed to form the nail head (e.g., a common round head for a **bright round wire nail**).
- Shanking/Shaping: The nail machine then cuts the wire to the precise length and forms the shank, which is typically cylindrical.
- Pointing: The other end of the nail is then pointed, usually into a diamond or chisel point, to facilitate easy penetration into target materials like wood or concrete. For specialized applications, **double pointed wire nails** are created.
- Surface Treatment (Optional): Depending on the application, nails undergo surface treatments. This includes galvanization for corrosion protection (creating **galvanised round wire nails** or **galvanized round head nails**), or heat treatment for increased hardness, especially for concrete nails.
- Tumbling/Polishing: Nails are tumbled to remove burrs and improve surface finish. Bright finish nails like **bright round wire nails** often undergo further polishing.
- Quality Control & Packaging: Nails are inspected for dimensions, strength, and finish, often adhering to standards like ISO 8974. They are then packaged for distribution, ready for **wire nail suppliers** and direct consumers.
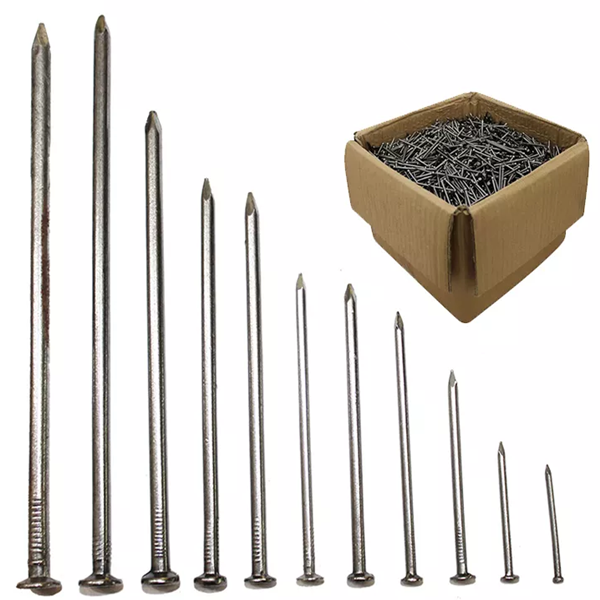

Figure 1: Illustration of wire nail manufacturing process, applicable to **common nail** production.
**Target Industries:** The output of this sophisticated manufacturing process serves diverse industries including construction (residential and commercial), furniture manufacturing, packaging, and general assembly. The service life of these nails, especially those treated for corrosion resistance, can extend for decades, contributing significantly to the durability of structures in petrochemical, metallurgy, and water supply & drainage applications where fasteners must withstand harsh environments. Advantages often include energy saving in construction by simplifying fastening, and significant corrosion resistance from galvanized variants.
Industry Trends and Technical Specifications
The fastener industry is continuously evolving, driven by demands for increased efficiency, material innovation, and sustainability. Current trends for **common nail** products include the development of higher-strength alloys for specialized applications, improved galvanization techniques for extended outdoor use, and the introduction of collated nail systems for pneumatic nailing tools, significantly speeding up construction processes. There's also a growing focus on the use of recycled materials in **wire nail** production to reduce environmental impact.
Key Technical Parameters for **Common Nail**
When specifying **common nail** types, several critical parameters must be considered to ensure optimal performance and structural integrity. These include material composition, shank diameter, length, head type, and point configuration. The **common nail sizes** are typically designated by "penny" (d) system in the US, ranging from small **3 common nail** to robust **60d nails**.
| Nail Size (Penny, d) | Length (inches / mm) | Shank Diameter (Gauge / mm) | Approx. Nails/lb | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6d common nail | 2" / 50.8 mm | 11.5 / 2.87 mm | 181 | Light framing, sheathing |
| 8d common nails | 2.5" / 63.5 mm | 10.25 / 3.25 mm | 106 | General framing, subflooring |
| 10d common nails | 3" / 76.2 mm | 9 / 3.76 mm | 69 | Framing, deck building |
| 16d common nail | 3.5" / 88.9 mm | 8 / 4.19 mm | 49 | Heavy framing, structural |
| 20d nails | 4" / 101.6 mm | 6 / 5.16 mm | 31 | Heavy timber construction |
| 40d nails | 5" / 127 mm | 4 / 6.04 mm | 18 | Large timber, heavy construction |
| 60d nails | 6" / 152.4 mm | 2 / 6.68 mm | 12 | Heavy-duty structural fastening |
The selection of the appropriate **common nail** is critical for ensuring structural integrity and longevity. Factors such as load-bearing capacity, shear strength, and withdrawal resistance must be considered, often guided by local building codes and engineering specifications. For instance, when you **nail wood to concrete**, specialized concrete nails with hardened shanks are required, highlighting the need for precise material matching.

Figure 2: Diverse types of nails, including **wire nails for wood**, showcasing various sizes and finishes.
Application Scenarios and Technical Advantages
The versatility of the **common nail** makes it indispensable across numerous sectors. Its primary function is to secure two or more materials, typically wood, through friction and mechanical interlock. Common applications include:
- Residential and Commercial Construction: Used extensively in framing walls, roofing, subflooring, and general carpentry. This includes using **8d common nails** for framing studs and **16d common nail** for heavier structural elements.
- Deck and Fence Building: Galvanized variants like **galvanised round head nails** or **galvanised wire nails** are crucial for outdoor structures where resistance to moisture and corrosion is essential.
- Packaging and Crating: **Iron wire nail** and **small wire nails** are commonly used in assembling wooden crates and pallets for shipping goods, providing robust and cost-effective fastening.
- Furniture Manufacturing: Certain types of **wire nail** are used in the assembly of wooden furniture, often selected for their discrete appearance and strong hold.
- Temporary Structures: For formwork, scaffolding, and other temporary constructions, the ease of installation and removal of **common nail** makes it a preferred choice.
- Specialized Applications: **Electrical wire nails**, for instance, are designed for specific electrical installation tasks where non-conductivity or other properties are desired.
Technical Advantages:
- High Shear Strength: The substantial shank diameter of **common nail** provides excellent resistance to shear forces, making it ideal for structural connections.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to screws or bolts, nails offer a significantly lower **common nail price** per unit, making them economically viable for large-scale projects.
- Ease of Installation: Nails can be quickly driven by hand or with pneumatic tools, greatly enhancing construction speed and labor efficiency.
- Material Compatibility: Designed for versatility, these nails effectively fasten a wide range of materials, particularly wood-to-wood applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: Options like **galvanised wire nails** provide superior protection against rust and degradation in outdoor or corrosive environments, extending the service life of the fastened components.

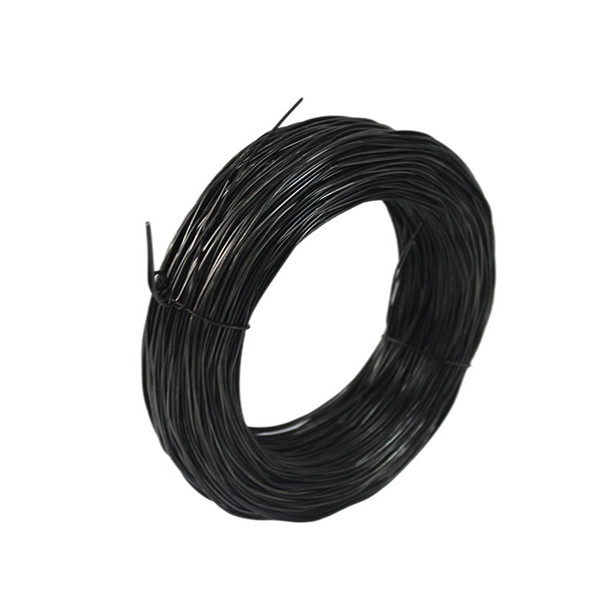
Figure 3: **Galvanised round wire nails**, showcasing their enhanced corrosion resistance for demanding applications.
Vendor Comparison and Customized Solutions
Selecting the right **wire nail suppliers** is crucial for ensuring consistent quality, competitive pricing, and reliable delivery. When evaluating **wire nail manufacturers**, B2B clients should consider several factors beyond just the **common nail price**.
Key Factors for Vendor Comparison:
- Certifications: Look for manufacturers with ISO 9001 quality management certifications and adherence to relevant ASTM or DIN standards. This signifies a commitment to quality and consistency.
- Material Traceability: Reputable suppliers should provide clear traceability of raw materials, ensuring the use of specified steel grades (e.g., mild steel wire nail).
- Production Capacity: Assess the manufacturer's ability to meet large volume orders and maintain consistent supply, especially for high-demand items like **10d common nails** or **4d common nail**.
- Customization Capabilities: The ability to provide bespoke solutions, such as specific lengths, shank treatments (e.g., ring shank for increased withdrawal resistance), or specialized coatings.
- Logistics and Delivery: Efficient global logistics and reliable lead times are critical for project planning and execution.
- Technical Support: Access to expert advice on nail selection, application, and troubleshooting can add significant value.
Customized Solutions:
Many projects require fasteners that deviate from standard specifications. Leading **wire nail manufacturers** offer customized solutions, including:
- Non-Standard Lengths and Diameters: Production of nails with precise dimensions, such as a **common nail 3** or a **common nail 1**, that are not commonly stocked.
- Specialized Materials: Use of high-strength alloys, stainless steel, or other specialized metals for demanding environments (e.g., marine or chemical processing).
- Custom Coatings: Application of proprietary coatings for enhanced corrosion resistance, specific color matching, or reduced friction during driving.
- Head and Point Configurations: Tailored head designs (e.g., checkered for better hammer grip) or point types (e.g., blunt for split prevention, sharp for hard materials).
- Packaging Solutions: Bulk packaging, collated strips (for pneumatic tools), or custom counts to streamline client's inventory and workflow.

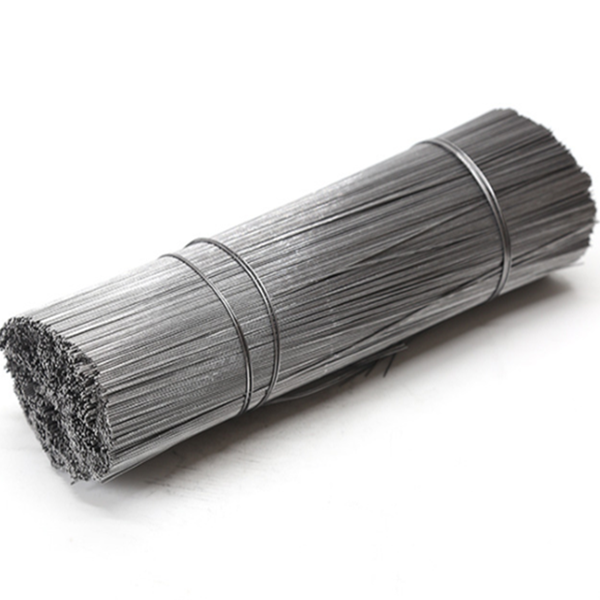
Figure 4: A selection of **iron wire nail** products, demonstrating different sizes and finishes available.
Application Case Studies: **Common Nail** in Action
Real-world applications underscore the critical role of the **common nail** in various industrial and construction projects. These case studies highlight not only the product's performance but also the advantages of partnering with reliable suppliers.
Case Study 1: Large-Scale Residential Framing
A major residential developer embarked on a project to construct 500 single-family homes. The primary challenge was to ensure structural integrity and rapid assembly while managing costs. By partnering with a leading **wire nail manufacturer** who supplied bulk quantities of 8d common nails and 16d common nails, the developer achieved significant efficiencies. The manufacturer's adherence to ANSI standards ensured consistent quality, reducing nail-related failures. The use of collated **wire nails for wood** with pneumatic nailers drastically cut labor time, contributing to a 15% reduction in overall framing costs and accelerated project completion by three weeks. The feedback from the construction team consistently praised the uniform driving performance and reliability of the nails.
Case Study 2: Marine Boardwalk Construction
A coastal city initiated the reconstruction of a 2-mile-long boardwalk, requiring fasteners capable of withstanding constant exposure to saltwater spray and high humidity. Standard nails would corrode rapidly. The solution involved specifying **galvanised wire nails** (specifically **galvanised nails 75mm**) with a heavy hot-dip galvanized coating. The chosen supplier provided certified products meeting ASTM A153 specifications for galvanization. After five years, an inspection revealed minimal corrosion on the fasteners, demonstrating the superior performance of the specialized galvanized nails and the efficacy of robust material selection for challenging environments. This project exemplifies the long-term cost savings and enhanced safety achieved by investing in appropriate, high-quality corrosion-resistant fasteners.
Case Study 3: Industrial Pallet Manufacturing
A prominent logistics company required custom-sized wooden pallets for transporting heavy industrial machinery. The pallets needed to be exceptionally strong to prevent damage during international shipping. The manufacturer worked closely with a **wire nail supplier** to develop a bespoke **iron wire nail** with a slightly larger diameter and a modified point for increased pull-out resistance from dense hardwoods. The nails were manufactured from a specific mild steel alloy to provide extra tensile strength without brittleness. This tailored fastening solution resulted in a 25% reduction in pallet failure rates during transit, significantly minimizing product damage and associated insurance claims. The client reported excellent experience with the customized approach, underscoring the value of a flexible and expert manufacturing partner.

Figure 5: A general view of various **common nail** types, showcasing the range of sizes and forms.
Trust and Reliability: FAQ, Lead Times, Warranty, and Support
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q1: What is the difference between **wire nails vs common nails**?
- A1: While often used interchangeably, "wire nail" is a broad term for any nail made from drawn wire. "Common nail" specifically refers to a type of wire nail characterized by a thick, heavy shank and a broad, flat head, designed for general construction and structural framing. Common nails are known for their strong holding power, especially in wood.
- Q2: How do I choose the correct **common nail sizes** for my project?
- A2: Nail size selection depends on the thickness of the materials being joined and the required holding power. A general rule of thumb is that the nail should be long enough to penetrate the receiving material by at least two-thirds of its length. Refer to our specification table (Table 1) for typical applications, e.g., **8d common nails** for general framing, **20d nails** for heavier timber.
- Q3: Are galvanized nails truly corrosion-resistant for outdoor use?
- A3: Yes, hot-dip galvanized nails, such as **galvanized round wire nails**, offer excellent corrosion resistance. The zinc coating creates a barrier and provides cathodic protection against rust, making them ideal for exterior applications like decks, fences, and siding. Always ensure the galvanization meets industry standards (e.g., ASTM A153) for optimal performance.
- Q4: Can these nails be used for **nail wood to concrete**?
- A4: Standard common nails are not suitable for concrete. For fastening wood to concrete, specialized concrete nails are required. These are typically made from hardened steel and often feature a fluted or knurled shank for better grip. Ensure you use the appropriate nail type to prevent bending or failure.
Lead Time and Fulfillment
Our commitment to efficient supply chain management ensures timely delivery for all orders. Standard **common nail** products typically have a lead time of 7-14 business days, depending on order volume and destination. For customized solutions or large-scale project orders, lead times will be provided upon consultation, factoring in specific material sourcing and production complexities. We leverage advanced logistics networks to ensure reliable and prompt fulfillment, minimizing downtime for your projects.
Warranty Commitments
We stand behind the quality of our **Concrete Nail & Wood Nails & Iron Nails & Wall Nails** products with a comprehensive warranty. All nails are guaranteed against manufacturing defects for a period of 12 months from the date of purchase. Our products are manufactured to stringent ISO 9001 quality standards, ensuring they meet or exceed specified mechanical properties and material composition. Any product found to be non-compliant with our published specifications will be replaced or refunded, subject to our terms and conditions. This commitment reflects our confidence in the durability and performance of our fasteners.
Customer Support and After-Sales Service
Our dedicated technical support team is available to assist with product selection, application guidance, and any post-purchase inquiries. With over two decades of experience as **wire nail manufacturers** and **wire nail suppliers**, our experts possess deep industry knowledge to provide tailored solutions. We offer comprehensive after-sales support, including troubleshooting, product performance analysis, and feedback channels to continuously improve our offerings. Your satisfaction and project success are our highest priorities. Contact us via phone or email for prompt and professional assistance.
References
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) B18.11, "Nails - Definitions, Terminology, and Data."
- ASTM International A153/A153M, "Standard Specification for Zinc Coating (Hot-Dip) on Iron and Steel Hardware."
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 8974, "Plain Shank Nails - Dimensions."
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) - Building and Fire Research Laboratory.
- Forest Products Laboratory, U.S. Department of Agriculture, "Wood Handbook - Wood as an Engineering Material."